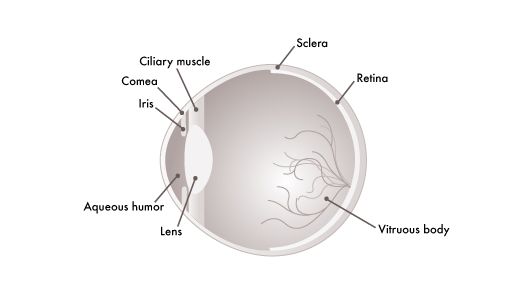
Other Information
Eye Anatomy and Issues
HOW WE SEE
Our vision occurs when our eye receives light rays reflected from an object. Light rays are refracted and focused onto the retina passing through the pupil and the lens. Retina is a tissue full of light sensitive cells, known as cones and rods, lining the inside of the back of the eye. These cells transfer the image into electrical energy and transmit those signals to our brain for interpretation through the optic nerve. The human eye can adjust its inner structure when looking at a near or distant object. When we look at a near object, the ciliary muscle is contracted and the lens is thickened. The lens power thus increases and we can look at a near object. On the other hand, when we look at a distant object, the ciliary muscle is relaxed and the lens is thinned. The lens power is then reduced and we can look at a distant object. This mechanism of changing the lens structure is called 'accommodation'.
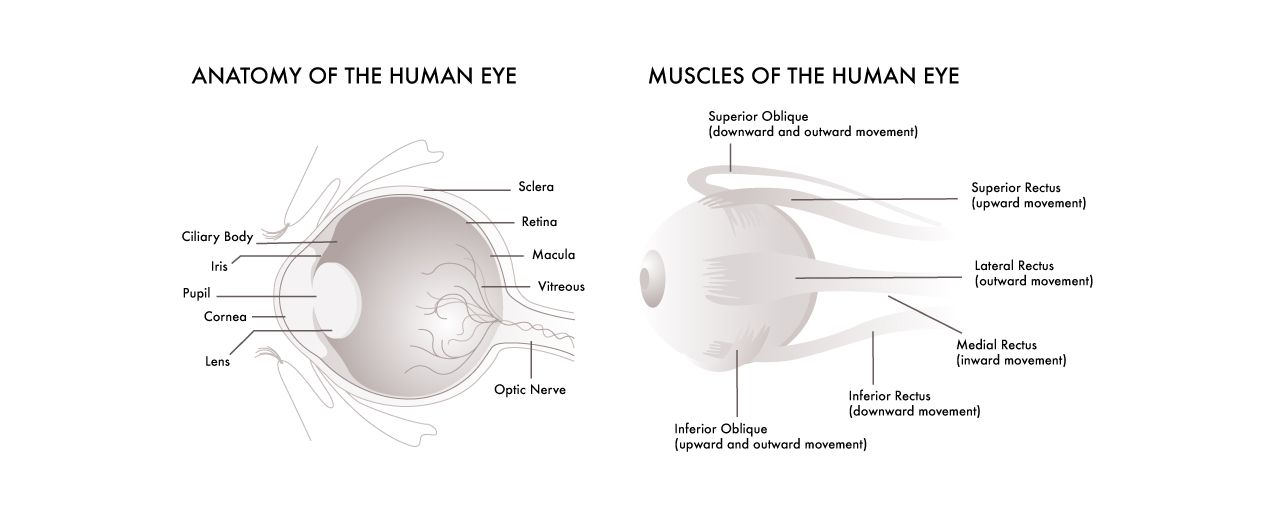
What makes up an eye?
CILIARY BODY AND MUSCLE
CILIARY BODY
The part of the eye that connects the choroid to the iris. Its main functions are accommodation, aqueous humor production and holding the lens in place.
IRIS
This is the colored part of our eye. It regulates the amount of light that enters the eye. Light enters through a central opening called the pupil. The iris contracts and expands to control the size of the pupil according to surrounding light.
PUPIL
The round, dark center of the eye. The iris controls the widening and narrowing (dilation and constriction) of the pupil.
CORNEA
The clear part of the eye covering the iris and pupil. It lets light into the eye, giving us sight. It refracts the light entering the eye onto the lens, which in turns focuses it onto the retina.
LENS
A transparent structure just behind the cornea. It focuses light rays onto the retina. Cataract takes place here. A cataract is when the lens becomes cloudy, and a cataract operation involves the replacement of the cloudy lens with an artificial plastic lens.
OPTIC NERVE
The nerve that carries electrical impulses from photoreceptor cells (cones and rods) in the retina to the brain. It connects our eye and brain with roughly 1.2 million nerve fibers.
VITREOUS
The vitreous body is part of the eye between the lens and the retina; it contains a clear jelly called the vitreous humor. The vitreous humor contains no blood vessels, and 98-99% of its volume is water (as opposed to only 75% in the cornea).
MACULAR
Macular is an oval-shaped highly pigmented yellow spot near the center of the retina.
SCLERA
Sclera is the white part of the eye, a tough covering with which the cornea forms the external protective coat of the eye.
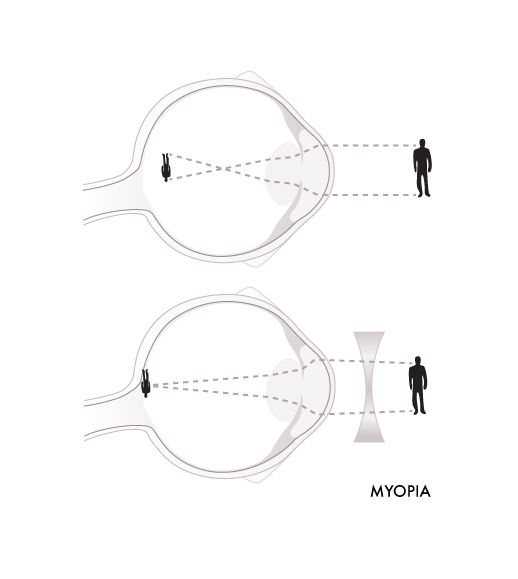
NEARSIGHTEDNESS (MYOPIA)
Nearsightedness, or Myopia, is the most common refractive error of the eye. In myopia, close objects look clear but distant objects look blurred. When Myopia occurs, it means that the eye does not bend or refract light properly to a single focus to see images clearly. Myopia can occur at any age; it is inherited and is often discovered in children aged from 8 to 12 years old. It can also occur in adults but between the ages of 20 and 40, there is usually little change in a person's myopia.
SYMPTOMS AND SIGNS
- Difficult to see distant objects clearly but can see close-up ones like words in a magazine
- Squinting, eye strain and headaches
- Feeling fatigued when driving or playing sports
CAUSES
For a normal eye, it focuses light rays on the retina but a nearsighted eye focuses the light rays in front of the retina. Reasons can be as below:
- Eyeball is too long
- Cornea or lens of the eye being too curved for the length of the eyeball
TREATMENT
If you suffer from myopic, you can wear glasses, contact lenses, or receive refractive surgery. It depends on the degree of your myopia, you may choose to wear glasses or contact lenses all day, or only when you feel you need to, for example, driving or attending classes. Our Single Vision glasses can help you correct your nearsighted problem. Our whole new level of clear lenses offer you extraordinary clarity with long-lasting performance and easy-to-clean convenience. Visit HERE to find out more.
Refractive surgery can reduce or even eliminate your need for glasses or contact lenses. The most common one is Lasik. If you are interested, please visit HERE to find out the details you need to know, including the pros and cons.
If your glasses or contact lens prescription begins with minus (-) numbers, like -2.50, you are nearsighted.
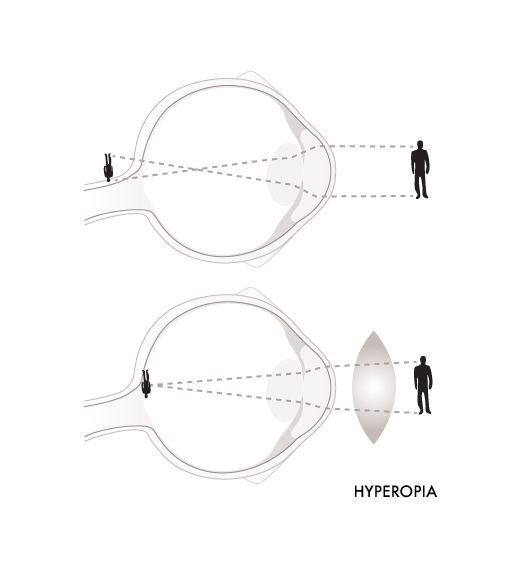
LONGSIGHTEDNESS (HYPEROPIA)
Longsightedness, or hyperopia, is a common vision problem with almost 1/4 of the population suffering from it. People suffering from longsightedness can see distant objects well but have difficulty focusing on close objects.
SYMPTOMS AND SIGNS
- Difficult to focus on a near object while can see a distant object well and clear
- Headaches, eye strain
- Squinting or feeling fatigued
Farsighted people sometimes have headaches or eye strain and may squint or feel fatigued when performing work at close range. If you get these symptoms while wearing your eyeglasses or contact lenses, you may need an eye exam and a new prescription.
CAUSES
For a normal eye, it focuses light rays on the retina but a longsighted eye finds difficulties in focusing a near object. So the light rays focus behind the retina instead. Reasons can be as below:
- The eye is shorter than a normal one
- The cornea is too flat
TREATMENT
Farsightedness can be corrected with glasses or contact lenses to change the way light rays bend into the eyes. Depending on the degree of your hyperopia, you can choose to wear glasses or contact lenses all day or only at the time you feel necessary. Using only the best premium material, our whole new level of clear lenses can pair with your up-to-date prescription to bring you the contentment of visual comfort, long-lasting performance, and easy-to-clean convenience. Visit HERE to find out more.
You can also choose to receive refractive surgery which can reduce or even eliminate your need for glasses or contact lenses. The most common one is Lasik. If you are interested, please visit HERE to find out the details you need to know, including the pros and cons.
If your glasses or contact lens prescription begins with plus (+) numbers, like +3.50, you are farsighted.
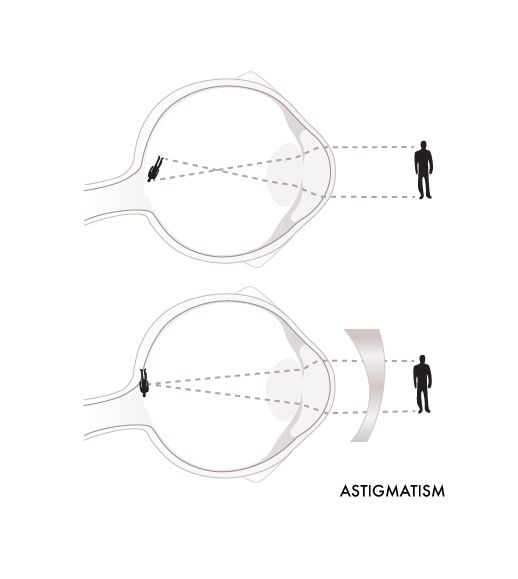
ASTIGMATISM
Astigmatism is a problem with how the eye focuses light. In an eye with astigmatism, it means light rays fail to come to a single focus on the retina to produce clear vision. Instead, the light rays come to multiple focus points, either in front of the retina or behind it, or both.
SYMPTOMS AND SIGNS
- Blurred or distorted vision at all distances.
- Eye strain and headaches especially after prolonged tasks like reading
- Squinting
CAUSES
For a normal eye, its cornea surface is smooth and curved evenly and focuses light rays on the retina at a single point. However, an astigmatism patient is unable to form a single point of focus on the retina. Reasons may be as below:
- Irregular shape of the cornea. The normal cornea is shaped like a baseball (a symmetrically round shape) but in astigmatism, it's shaped like a football
- Irregular shape of the lens inside the eye
TREATMENT
Astigmatism can be corrected by wearing a pair of cylindrical lenses. A cylindrical lens (CYL) is used to correct the difference between the powers of the two principal meridians of the eye. If you like to know more about meridians, please visit HERE . Our Single Vision glasses can help you correct your astigmatism problem. Our whole new level of clear lenses offer you maximum visual acuity and long-lasting performance. Visit HERE to find out more.
Another common treatment for astigmatism is wearing contact lenses. Nowadays, soft lenses called toric contact lenses can correct astigmatism. But if you have severe astigmatism, rigid contact lenses may be a better choice. Gas permeable contact lenses can also be an alternative because these lenses are rigid and optically replace the cornea as the refracting surface of the eye.
You can also choose to receive refractive surgery which can reduce or even eliminate your need for glasses or contact lenses. The most common one is Lasik. If you are interested , please visit HERE to find out the details you need to know, including the pros and cons.
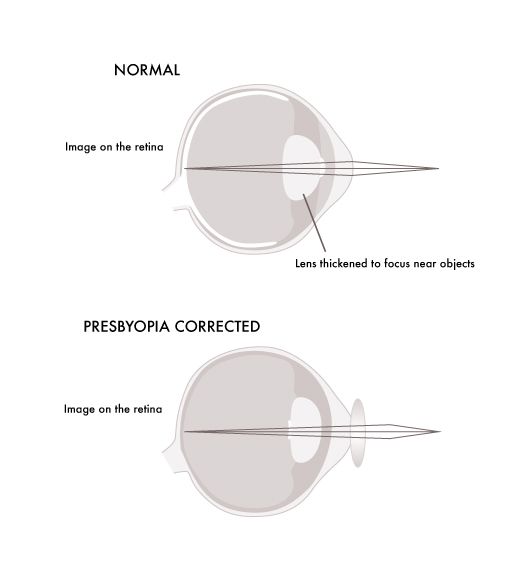
PRESBYOPIA
Presbyopia (literally means "aging eye") is an age-related eye condition that makes it more difficult to see an object very close. It usually occurs after the age of 40 when people receive blurred near vision when they read at close range. The main reason is the lens becomes more rigid and can't change its shape as easily as it once did.
SYMPTOMS AND SIGNS
- Feeling much comfortable to hold books, magazines or other reading materials at arm's length in order to focus properly
- Headaches, eye strain or feeling fatigued from up-close work
CAUSES
Presbyopia and Hyperopia look similar but they are caused by different things. Hyperopia is a refractive error that occurs when the eye is shorter than normal or has a cornea that is too flat. And hyperopia is usually present from birth, while presbyopia develops later, usually after age 40.
- Age related process that makes the eye's lens more rigid
- Muscles surrounding the lens also have lose its elasticity
- Lens gradually becomes less flexible and hard to change its shape as easy as before, thus the eye has a harder time focusing on up-close objects
TREATMENTS
Eyeglasses with bifocal or progressive lenses are the most common method of correcting presbyopia. Bifocal lenses have two different points of focus. The upper part of the eyeglass lens is set for distance vision, while the lower part has a prescription tailor-made for seeing up-close work. Progressive lenses are similar to bifocal lenses, but they offer a more gradual visual transition between the two prescriptions, and with no visible line between them. Glasses Gallery offers you premium bifocal and progressive lenses that give you an eclectic and ingenious adaption to pep up your life.
Reading glasses are another choice. Unlike bifocals and progressives, reading glasses usually are worn just during up-close work.
Another way to correct presbyopia is multifocal contact lenses, available in gas permeable or soft lens materials. Multifocal contact lenses create multiple levels of corrective power. Also, there's monovision contact lenses in which one contact lens is set for distance while the other is for near vision. The brain learns to favor one eye or the other for different tasks.
On the other hand, surgical options to treat presbyopia are also available. One is called conductive keratoplasty or CK. It uses radio waves to create more curvature in the cornea for a higher "plus" prescription to improve near vision and is very effective in treating presbyopia. However, the correction is temporary and diminishes over time.
Another option is Lasik. It is used to create monovision, in which one eye is corrected for near vision while the other eye is set for distance vision. If you are interested in, please visit HERE to find out the details you need to know, including the pros and cons.
SENIOR EYE CARE
Our body will not always be as strong and the same is with our eyes and vision. Though it's inevitable to age, we can well prepare ourselves for any upcoming eye health issues. To ensure we have a good vision, we not only need to perform an annual eye exam but also need to pay attention to any obvious signs and symptoms. The common age-related vision changes are listed below:
-
MORE LIGHT NEEDED
Require brighter lighting to help reading as well as other tasks
-
NOTICEABLE GLARE
More glare formed because the crystalline lens in our eye becomes more scattered
-
COLOR SHIFTS
Difficult to identify certain shades of colors because of the discolored crystalline lens
-
REDUCED TEAR PRODUCTION
As we age, the tear glands in our eyes will form less tears. Artificial tears might come in handy to help
COMMON EYE ISSUES AS WE AGE
CATARACTS
A cataract is a clouding of the eye's natural lens, which lies behind the iris and the pupil. The lens must be clear in order to focus light properly for us to see clearly. If the lens becomes cloudy, we'll get a blurred vision and this is called a cataract. It is not a rare eye issue among older people, and the surgery is one of the most common and successful medical procedures in the world.
GLAUCOMA
Glaucoma is a disease that damages your eye's optic nerve. It occurs when fluid builds up in the front part of the eye and causes higher-than-normal fluid pressure. Glaucoma is a dangerous eye issue if left untreated.
AGE-RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION
Age-related macula degeneration (AMD) is a deterioration of the eye's macula. The macula is the central part of the retina. AMD affects one's central vision which allows people to see fine details clearly. It begins when people start seeing distortion of straight lines.
CHILDREN'S EYE CARE
Glasses Gallery is a fervent supporter of children's eye care. Children are vulnerable yet precious; their vision is intrinsic to every successful step they take in their lives; we need to provide them with delicate, comprehensive eye care for a healthy, vibrant growth to brighten their future. We want to guarantee both the present and future perfect with no past regret.
WHEN SHOULD CHILDREN HAVE THEIR VISION CHECKED?
- First comprehensive eye exam: At the age of 3
- Follow up eye exam: before first grade, by the age of 5 or 6
- Regular eye exam: every two years if no vision correction is needed; children who wear eyeglasses or contact lenses should get eye exam annually or as recommended by the eye doctor or optometrist
SIGNS OF VISION PROBLEMS IN CHILDREN
- Rubbing of the eyes
- Frequent headache
- Squinting
- Tilting the head to see better
- Holding objects or books unusually close or far away
- Cannot follow the lines while reading or need to use finger to guide the eyes
- Excessive blinking
- Complaining of tired eyes
- Favoring one eye by covering it or turning their head
- Eyes that are not aligned or are not working together
- Sensitive to light and/or excessive tears
- Avoid activities that require near or distant vision, e.g. reading a book or playing ball
- Red, swollen or encrusted eyes
- Recurring styes or infections on eyelids
Did you know?
UV and other radiation from the sun can also harm the eyes, and children need UV protection even more than adults. Children in general spend more time outdoors than adults, hence always remind them to use sunblock, wear sunglasses and if possible, wear a hat. What parents need to know is that the damage done to children's eyes can be far more serious than to adults. Children are more susceptible to retinal damage from UV rays since the lens inside a child's eye is much clearer than that of the adult, thus letting more UV enter deep into the eye. If safeguarding the healthy development of your children's vision is your concern, our kids sunglasses are the way forward. We offer sunglasses that can individually prescribed to fit your child's optical needs, plus the total block of UVA/UVB, and that every pair is finely polished with Anti-Reflective and Anti-Scratch Coatings to best enhance the perfect vision. Clickif you like to look for the ideal shades for your child now.
Disease
EYE ISSUES
The eye is a very complex organ made up of many parts to create a clear vision. Usually at some point in our lives we have encountered some issues, some go away on its own, while others need to be treated by a doctor. One thing is, no matter how minor the symptoms are, it's never a good idea to just leave them untreated. Always check them out and don't leave yourself in the dark as the consequences can be serious.
AGE-RELATED VISION PROBLEM
Cataracts
A cataract is a clouding of the eye's natural lens, which lies behind the iris and the pupil. The lens must be clear in order to focus light properly for us to see clearly. If the lens becomes cloudy, we'll get a blurred vision and this is called a cataract. It is not a rare eye issue among older people, and the surgery is one of the most common and successful medical procedures in the world. Symptoms of cataracts may include faded colors, blurred or distorted vision, halos around light, trouble with bright lights, and trouble seeing at night. It further leads to an increased sensitivity to glare or the feeling of having a film over the eyes.
Cataracts are the most common cause of vision loss in people over age 40 and is the principal cause of blindness in the world. Cataracts are mainly age-induced but besides advancing age, other risk factors may include:
- Ultraviolet radiation from sunlight and other sources
- Diabetes
- Hypertension
- Obesity
- Smoking
- High myopia
- Significant alcohol consumption
MODERATE VISION PROBLEMS
Dry Eye
Dry eye (or being called "dry eye syndrome"/"dry eye disease") is caused by a continuous lack of lubrication and moisture on the surface of the eye. Dry eye can cause various degrees of discomfort, ranging from minor itchiness, constant eye irritation, significant inflammation to even scarring of the surface of the eye.
Eye Floaters
Eye floaters are those tiny spots, strings, or "cobwebs" that drift aimlessly around in your view. In general, they are common and not dangerous but eye exams are recommended.
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis, also known as pink eye, is inflammation of the thin, clear covering of the white of the eye and the inside of the eyelids (conjunctiva). It is commonly due to an infection (usually viral, but sometimes bacterial) or an allergic reaction. Conjunctivitis can affect one or both eyes, symptoms include watery (and/or burning) itchy eyes, and sticky yellow eye discharge. Usually viral conjunctivitis requires no medical treatment while antibiotic eye drops or ointments are needed for bacterial conjunctivitis.
SEVERE VISION PROBLEMS
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a disease that damages your eye's optic nerve. It occurs when fluid builds up in the front part of the eye and causes the higher-than-normal fluid pressure inside the eye. Glaucoma usually has few or no initial symptoms but it's a dangerous eye issue if left untreated as it can eventually lead to blindness. The disorders can be roughly divided into two main categories: "open-angle" and "closed-angle" (or "angle closure") glaucoma. Open-angle chronic glaucoma is sometimes called "the silent thief of sight" because there are no obvious warning signs in the early stages — no pain or vision loss, simply no hints that something is wrong at all. Open-angle glaucoma is treated with either glaucoma medication to lower the pressure, or with various pressure-reducing glaucoma surgeries.
Closed-angle glaucoma, however, is characterized by sudden eye pain, red eyes, halos around lights, dilated pupils, nausea and vomiting, and other symptoms resulting from a sudden spike in the eye's internal pressure, known as intraocular pressure (IOP), and is treated as a medical emergency. If the pressure is not reduced within hours, it can cause permanent vision loss.
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic Retinopathy is a vision-threatening damage to the retina of the eye caused by diabetes. At an early stage, it may cause blurred vision. As the disease progresses, you may notice a cloudiness of vision, blind spots. or floaters. Diabetic retinopathy can cause complete blindness if not treated, so go for a regular eye checkup especially if you are a diabetic or if your family has a history of diabetes.
Retinal Detachment
Retinal Detachment refers to a situation when the retina becomes separated from its underlying supportive tissue. The retina cannot function when these layers are detached, and unless it is reattached soon, the situation may result in a permanent vision loss.
If you suddenly see a shadow or a curtain dropping from the top of the eye or from the side of the eye, you need to see a doctor right away. Other signs include seeing spots, floaters, flashes of light, and blurred vision. Retinal detachment does not associate with any pain, but if you experience any of the aforementioned signs, you need to seek professional help immediately.
Age-related Macular Degeneration
Age-related macula degeneration (AMD) is a deterioration of the eye's macula. The macula is the central part of the retina. AMD affects one's central vision which allows people to see fine details clearly. It usually produces a slow, painless loss of vision. In rare cases, sudden vision loss can happen. Early signs include seeing shadowy areas or unusually fuzzy vision like distorted straight lines. Up to this present day, there's no complete cure for AMD but some treatments are available to delay its progression or even improve vision.